Early Seals' Whiskers: Clues to Ancient Underwater Feeding
TL;DR Summary
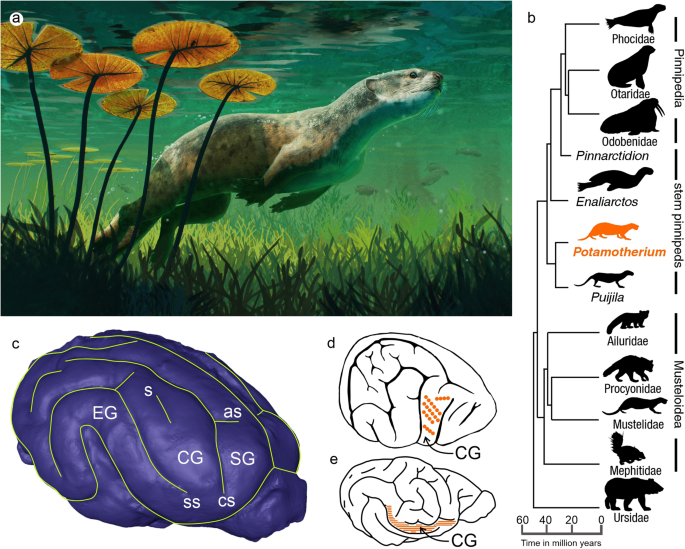
Fossil brains of early seals, known as pinnipeds, provide evidence of their underwater feeding behavior and the importance of their whiskers (vibrissae) in locating prey. The study analyzed the brain anatomy of fossil and extant carnivorans and found that the reliance on whiskers in modern pinnipeds is an ancestral feature that aided the survival of early seals in marine habitats. This research sheds light on the ecological transition of pinnipeds from terrestrial to amphibious marine species and the adaptations necessary for underwater foraging.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
6
Time Saved
31 min
vs 32 min read
Condensed
99%
6,256 → 83 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com