The Impact of Genome Doubling on Cancer Development and Chromatin Segregation.
TL;DR Summary
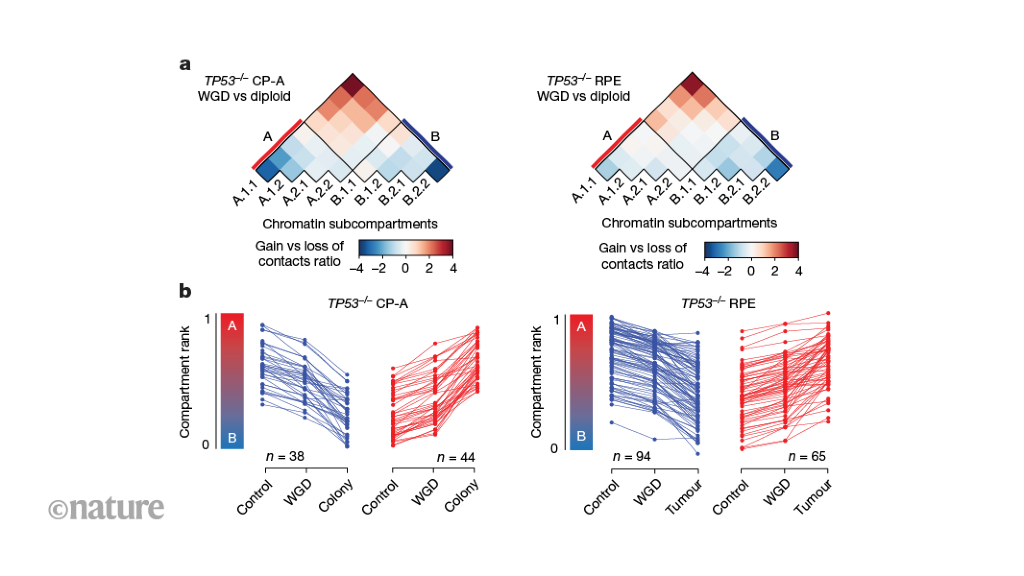
Cells with doubled genomes experience a shortage of proteins that regulate DNA packing, leading to poor segregation of DNA structures and contributing to cancer development. The cells do not upscale protein synthesis to cope with the increase in DNA, according to a study published in Nature.
Topics:science#cancer-development#chromatin-segregation#dna-packing#genome-doubling#health#protein-synthesis
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
1 min
vs 2 min read
Condensed
84%
287 → 46 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com