Discovery of Eclipsing Absorber Sheds Light on NGC 6814's Active Galaxy
TL;DR Summary
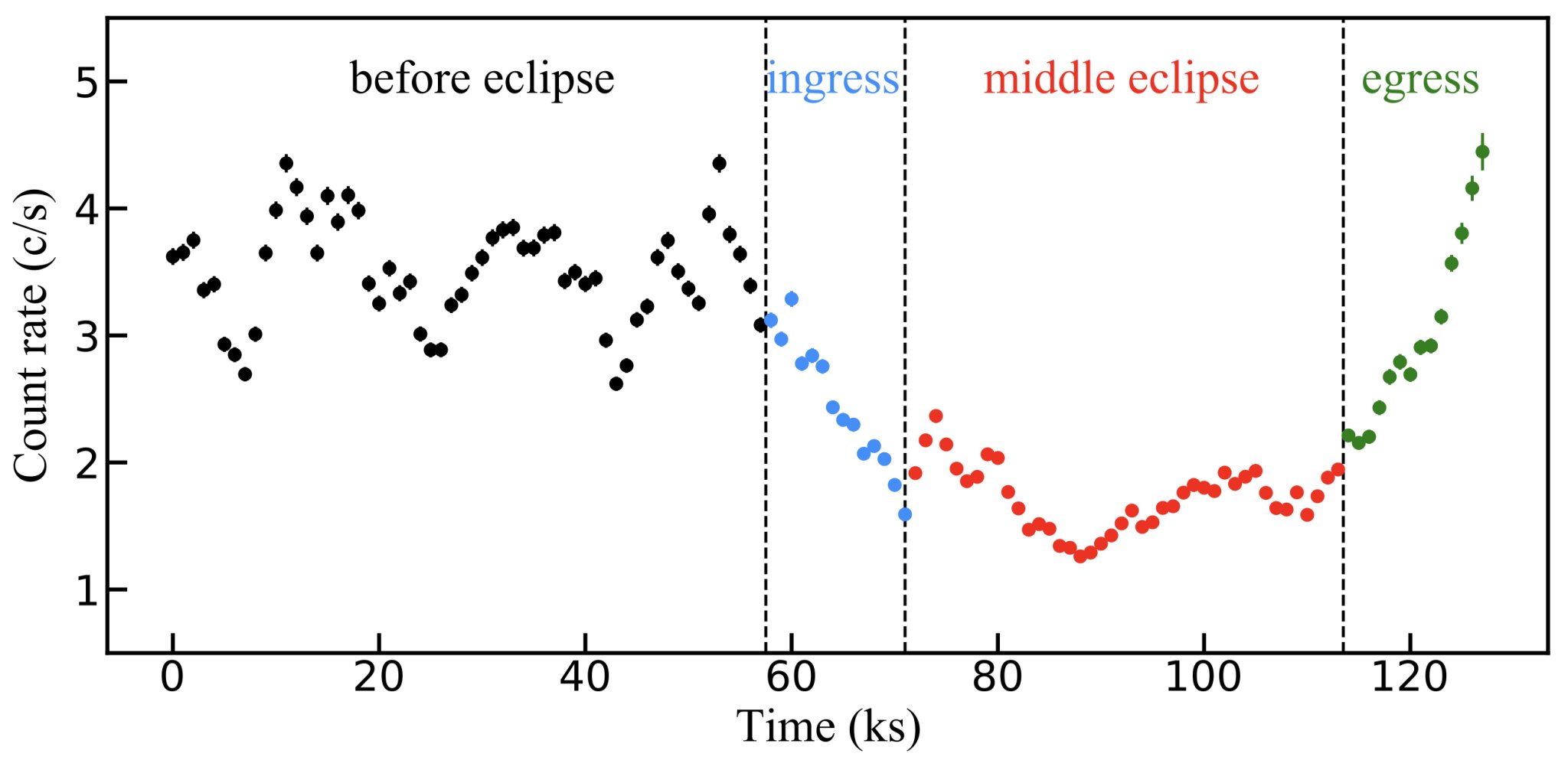
Astronomers have discovered a composite eclipsing absorber in the active galaxy NGC 6814, responsible for a distinct X-ray eclipse event. The absorber is a clumpy, multi-phase cloud cluster, possibly part of the disk "wind" launched from the inner region of the accretion disk. The research team used a flux-color plot to analyze the eclipse event and revealed the presence of Compton-thick absorption, previously unnoticed in the spectra. This study highlights the importance of X-ray occultation events in understanding the gas surrounding supermassive black holes.
Topics:science#active-galaxy#astronomy#eclipsing-absorber#ngc-6814#supermassive-black-hole#x-ray-eclipse-event
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
0
Time Saved
3 min
vs 4 min read
Condensed
88%
724 → 84 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org