Advancements in Whole Genome Sequencing for Early Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders in Infants
TL;DR Summary
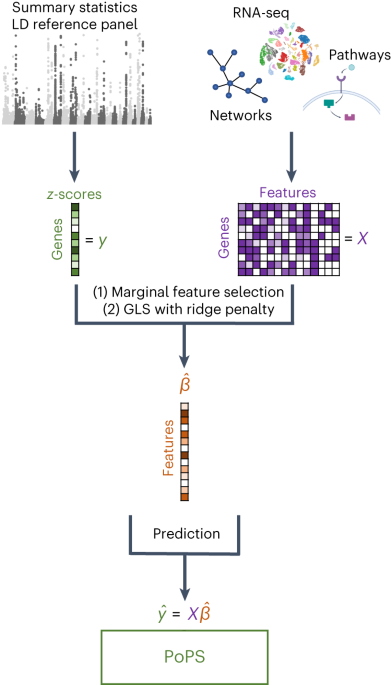
Researchers have developed a method called PoPS (Polygenic Prioritization of Gene Features) that leverages polygenic enrichments of gene features to predict genes underlying complex traits and diseases. The method utilizes various data sources, including genetic association studies, gene expression data, and functional annotations, to prioritize candidate genes. The researchers have made the processed gene features, visualizations, and code available on GitHub, as well as the PoPS results for multiple complex traits and diseases. This approach provides a valuable tool for understanding the genetic basis of complex traits and diseases.
Topics:health#complex-traits#diseases#gene-features#geneticsgenomics#polygenic-enrichments#predictive-modeling
- Leveraging polygenic enrichments of gene features to predict genes underlying complex traits and diseases Nature.com
- Infant Rapid Genome Sequencing Yields More Diagnoses Than Targeted Gene Panels, Study Finds GenomeWeb
- A new study sees potential in DNA sequencing of infants STAT
- Whole genome sequencing shows promise for early diagnosis of genetic disorders in newborns, infants News-Medical.Net
- Testing Entire Genome Twice as Good at Spotting Genetic Disorders as Targeted Tests Are U.S. News & World Report
- View Full Coverage on Google News
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
20 min
vs 21 min read
Condensed
98%
4,053 → 89 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com