"MIT's Breakthrough: Simple Superconducting Device to Revolutionize Computing Energy Efficiency"
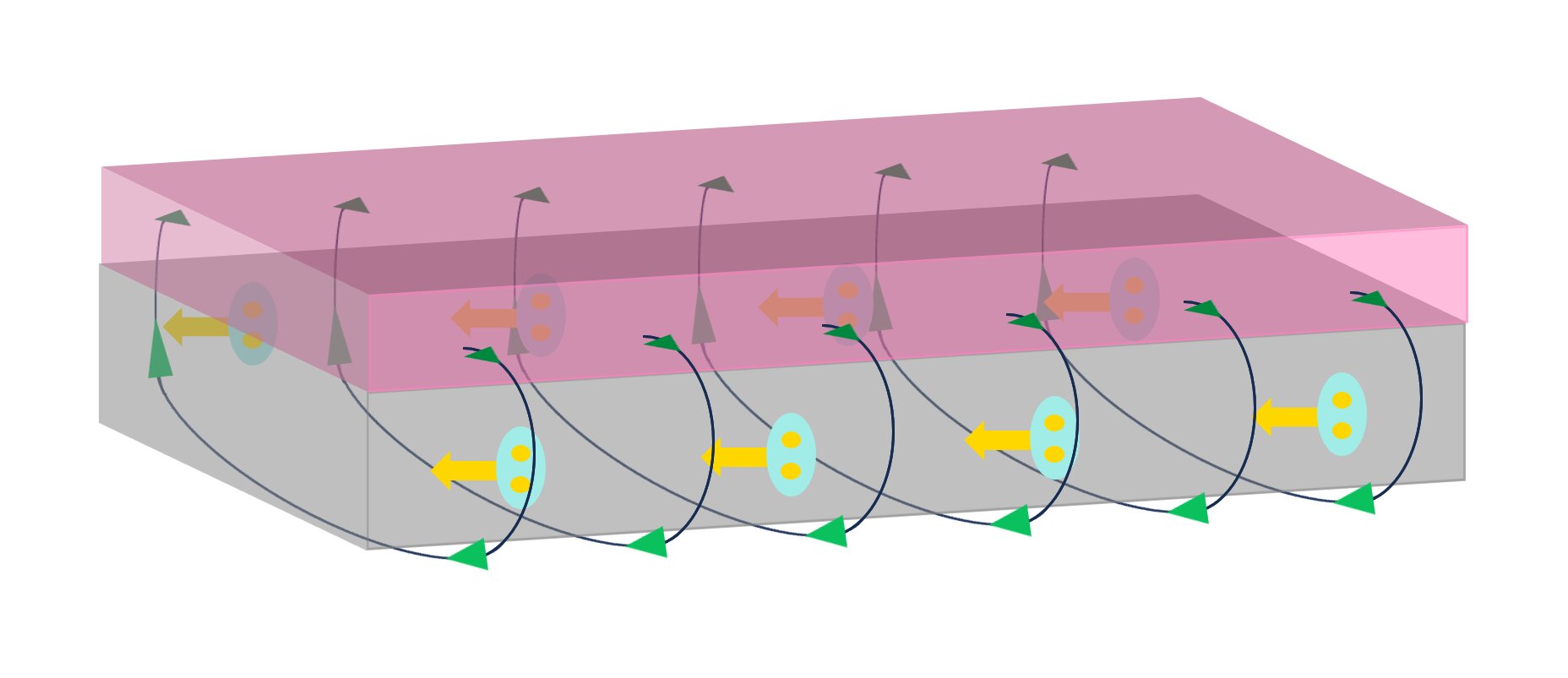
Researchers at MIT have developed a superconducting diode that could significantly reduce energy consumption in high-power computing systems. The diode, which is more than twice as efficient as similar ones reported by others, utilizes the Meissner screening effect and edge asymmetries within superconductors to create a non-reciprocal current flow. This breakthrough could have implications for quantum computing technologies and offers a straightforward approach to improving energy efficiency in computing systems. The nanoscopic diode is easily scalable and could be produced in large quantities on a single silicon wafer.