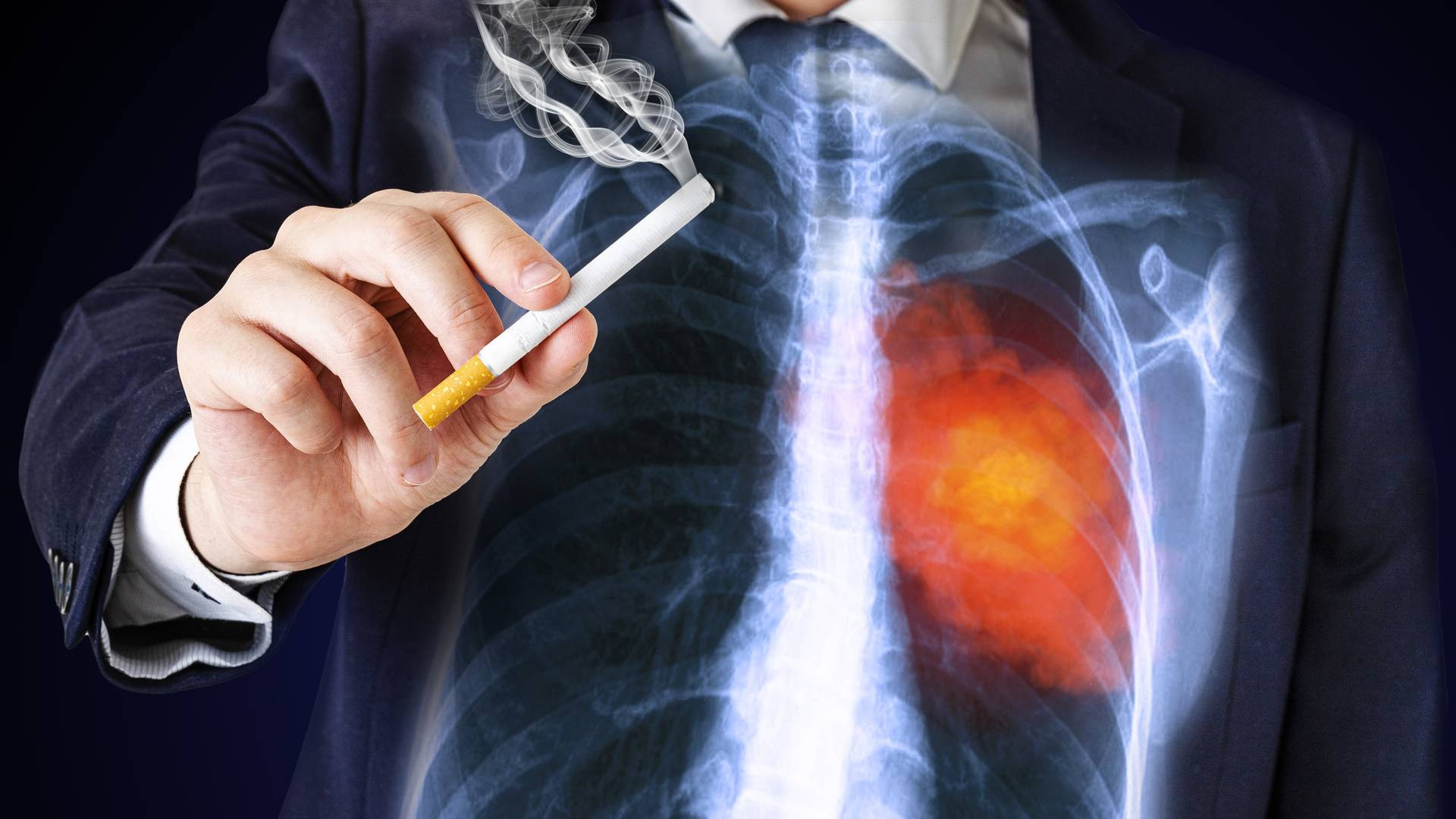
Smoking's DNA Mutations Fuel Cancer Growth, Study Finds
A new study confirms that smoking tobacco can cause DNA mutations, known as "stop-gain mutations," that lead to cancer. These mutations instruct the body to stop producing specific proteins, hindering their ability to protect against cancer. The study also found that tumor-suppressor genes, which produce proteins that block abnormal cell growth, were particularly affected by these mutations, resulting in uncontrolled cancer cell proliferation.
