Unveiling the Role of MOF in Enhancing Mitochondrial Integrity and Function
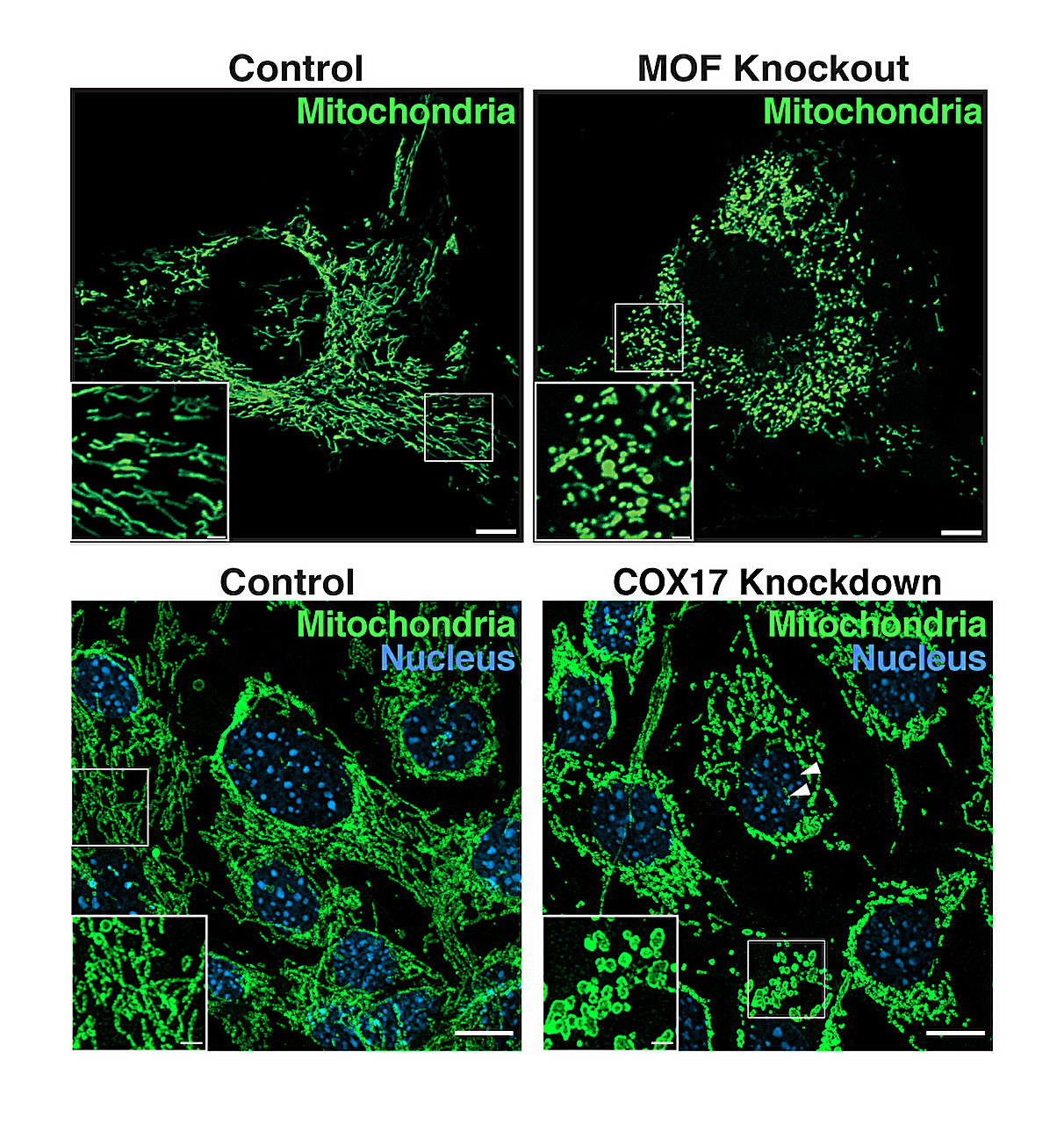
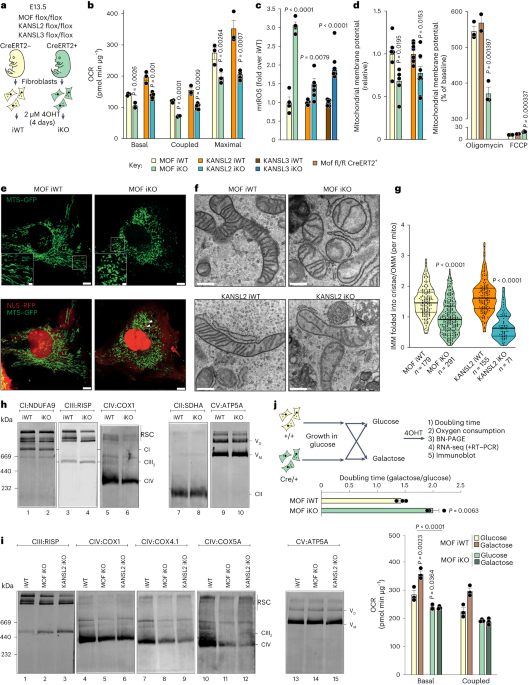
The MOF-KANSL complex, which plays a role in transcriptional regulation, has been found to be crucial for maintaining mitochondrial integrity and function. Loss of MOF or KANSL complex members in primary cells resulted in altered mitochondrial respiration, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS), reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, fragmented mitochondrial morphology, and decreased cristae density. The MOF-KANSL complex was also found to be important for the assembly and stability of respiratory supercomplexes. Furthermore, the study identified COX17 as an acetylation target of MOF, and acetylation of COX17 was shown to promote mitochondrial respiration. These findings provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying mitochondrial dysfunction and highlight the importance of protein acetylation in maintaining mitochondrial health.