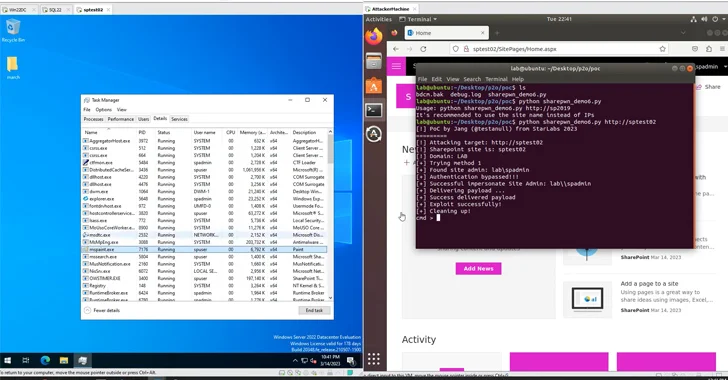
Researchers link leak to rise in Microsoft SharePoint attacks and ransomware use
Researchers suggest that a leak of exploit details, possibly from a Pwn2Own competition, allowed attackers including Chinese spies and ransomware groups to exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft SharePoint before patches could fully prevent the attacks, leading to widespread compromises and ongoing security concerns.