Uncovering the Gut Microbiome's Role in Enhancing Cancer Immunotherapy
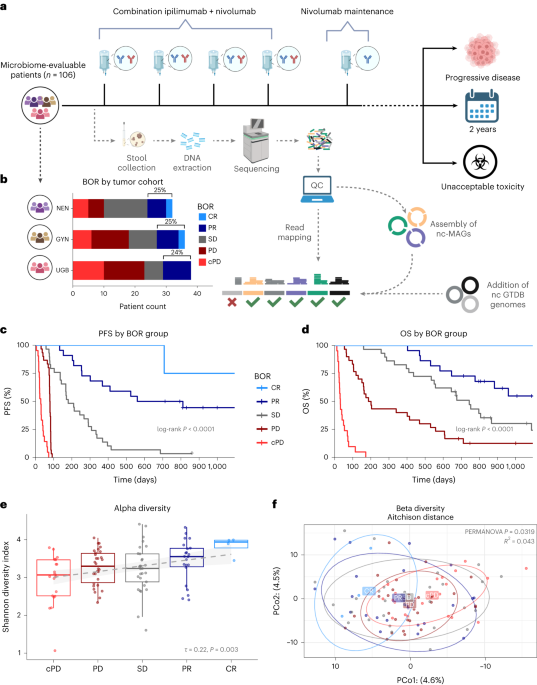
A study has found that the composition of a patient's gut microbiome may serve as a predictive biomarker for the efficacy of combination immune checkpoint blockade (CICB) across various cancer types. By analyzing the gut microbiomes of patients receiving CICB, researchers discovered strain-level microbial abundance signatures associated with treatment response, which were consistent across different cancer subtypes. The study suggests that these microbial signatures may be valuable in predicting patient responses to CICB and guiding treatment decisions.
