"Primate-specific RNA polymerase II elongation factor found in new human gene cluster sequence"
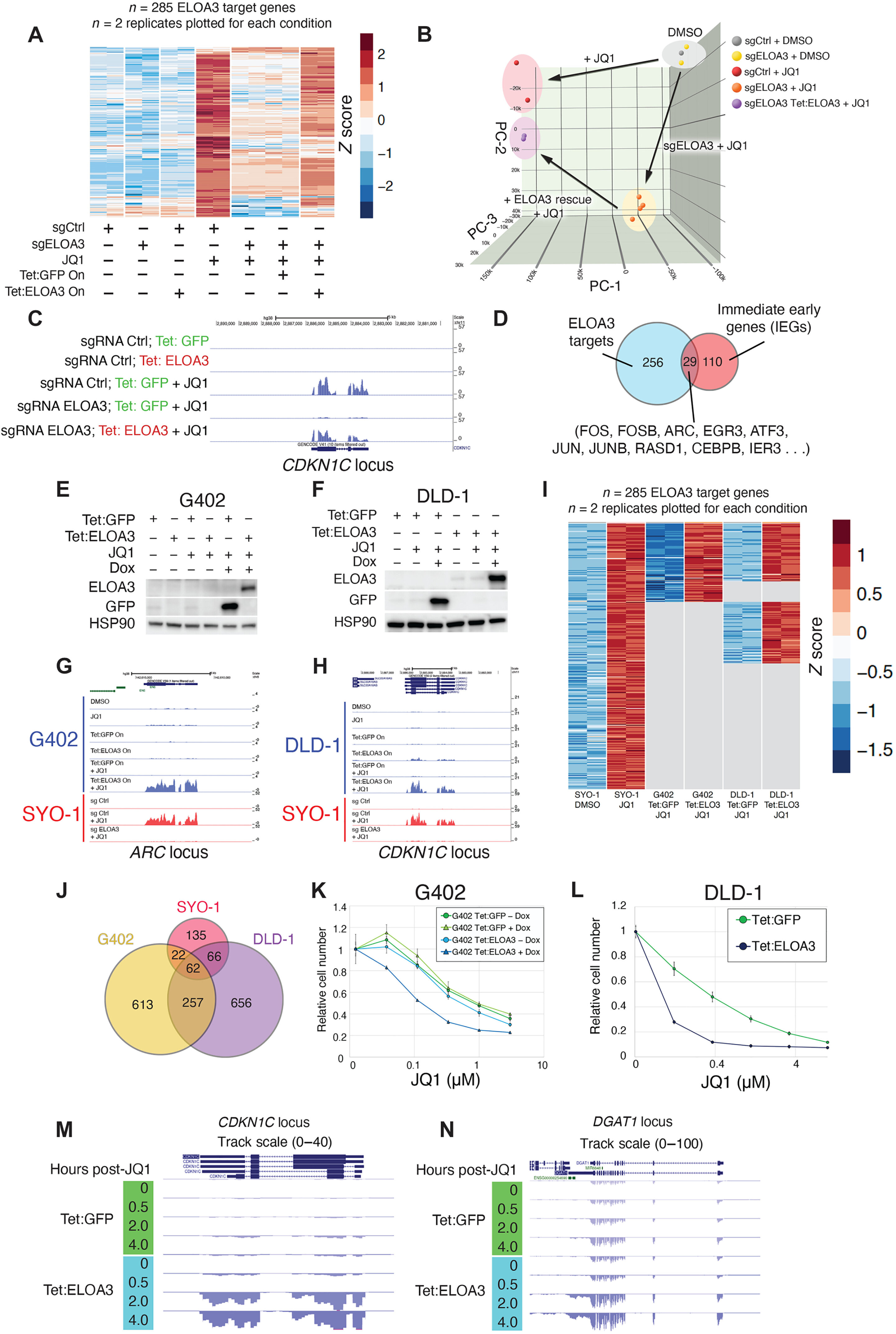
Researchers have discovered a new repeat gene cluster sequence that is exclusively expressed in humans and non-human primates. The discovery has implications for understanding transcriptional regulation, human evolution, and repetitive DNA sequences. The gene cluster encodes the protein Elongin A3 (ELOA3), which is closely related to a protein previously studied for its role in regulating gene expression. The number of ELOA3 gene repeats varies among individuals and primate species, suggesting concerted evolution and gene homogenization. The discovery enhances our understanding of the human genome and opens up possibilities for targeted drug design in cancer. Further research will explore the expression of ELOA3 in genomes and its potential role in developmental disorders and diseases.
