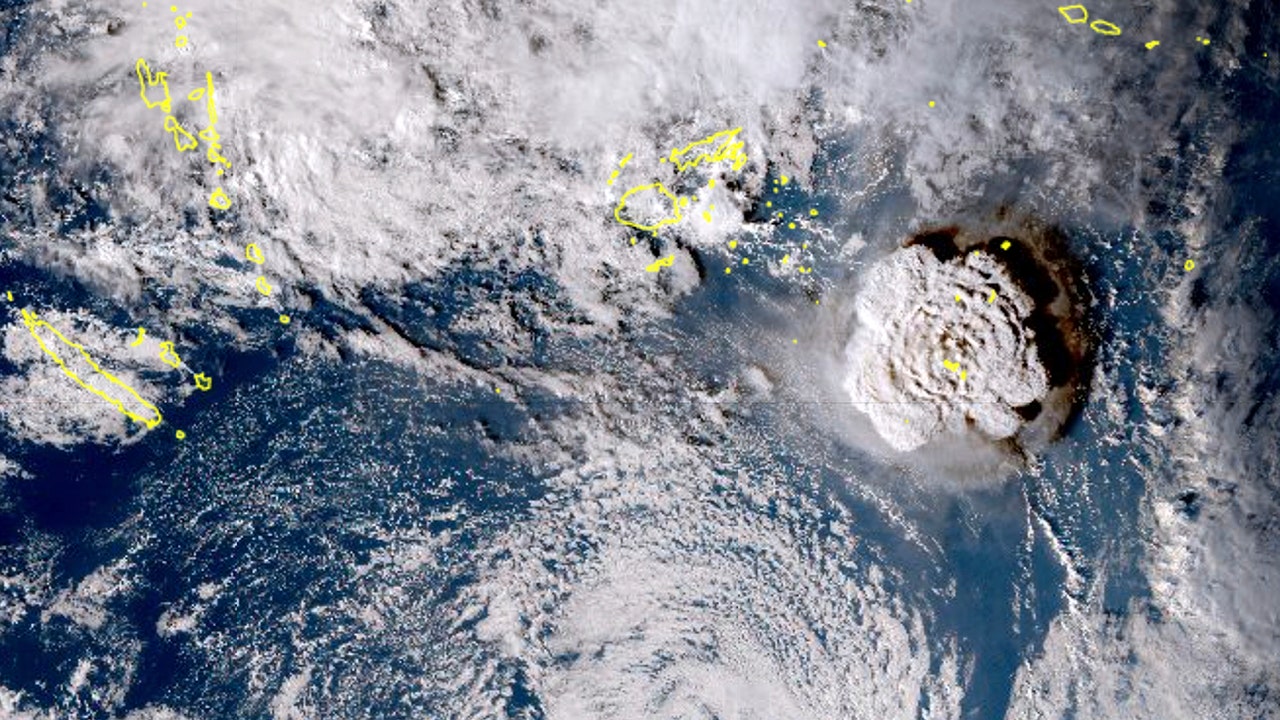
Tonga's Undersea Volcano Disrupts Satellite Signals Worldwide
The undersea volcano eruption in Tonga last year disrupted satellite signals halfway around the world, according to an international team of researchers. They used satellite- and ground-based observations of the ionosphere to demonstrate that an air pressure wave triggered by volcanic eruptions could produce an "equatorial plasma bubble," which severely disrupts satellite-based communications. An equatorial plasma bubble can delay radio waves as well as degrade the performance of GPS. The findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
