Active Exploitation of Critical MongoDB Vulnerability CVE-2025-14847
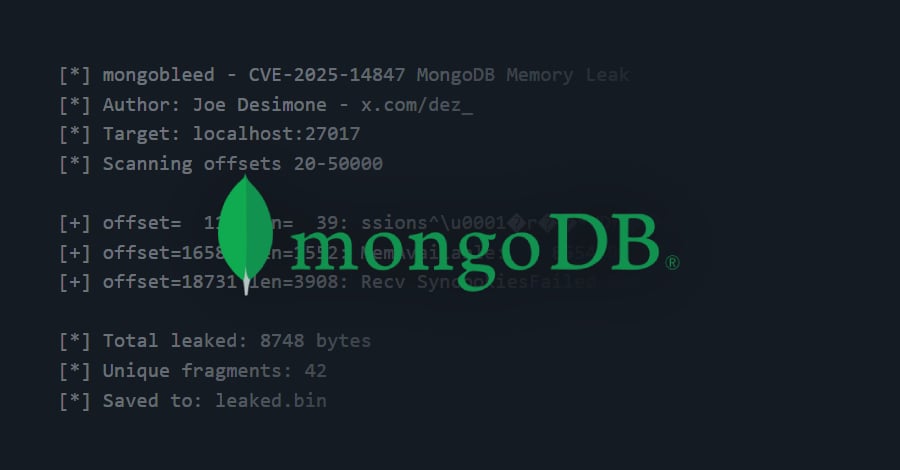
A critical vulnerability in MongoDB, CVE-2025-14847, allows unauthenticated attackers to remotely leak sensitive data by exploiting a flaw in zlib compression, with over 87,000 instances potentially affected worldwide. Users are advised to update their MongoDB versions and implement mitigations such as disabling zlib compression and restricting server exposure.





