Global Climate Interconnections: Mapping the Danger Zones
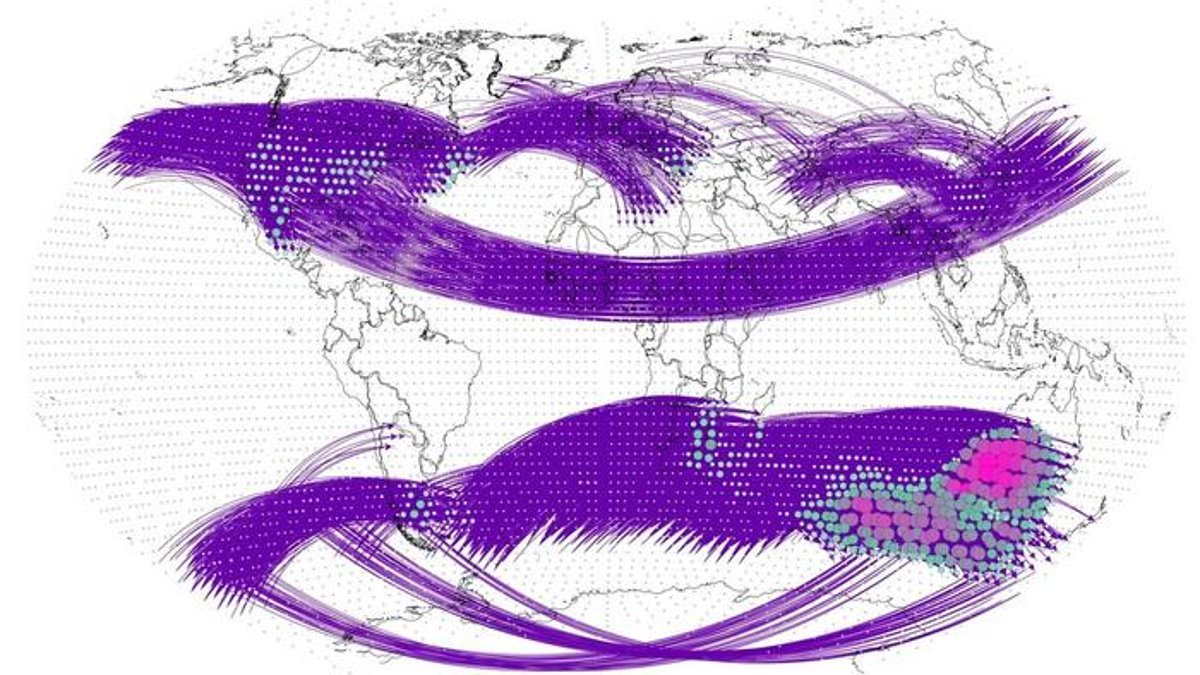
Certain areas of the world are identified as "hotspots" for interlinked extreme weather events, known as teleconnections, which can have a domino effect on a global scale. Researchers from Beijing Normal University have used a climate network analysis method to identify regions significantly affected by these interconnected events, such as southeastern Australia and South Africa. The impact of teleconnections has been increasing, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere, possibly due to climate change and human activities. The findings aim to help predict and address future climate challenges. Additionally, a separate study warns that rising global temperatures could make the US East Coast and Middle America unlivable by 2100, leading to increased health risks and fatalities.

