"Revolutionizing Antibody Evolution with Protein Language Models"
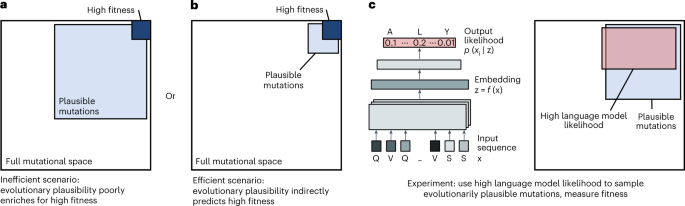
Researchers have used protein language models to guide the directed evolution of human antibodies with unprecedented efficiency. The language models were used to identify plausible amino acid substitutions that were experimentally screened for improved fitness. The researchers evolved seven human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies that bind to antigens from coronavirus, ebolavirus, and influenza A virus. The affinity of all antibodies was improved after measuring only 20 or fewer new variants of each antibody across just two rounds of evolution.
