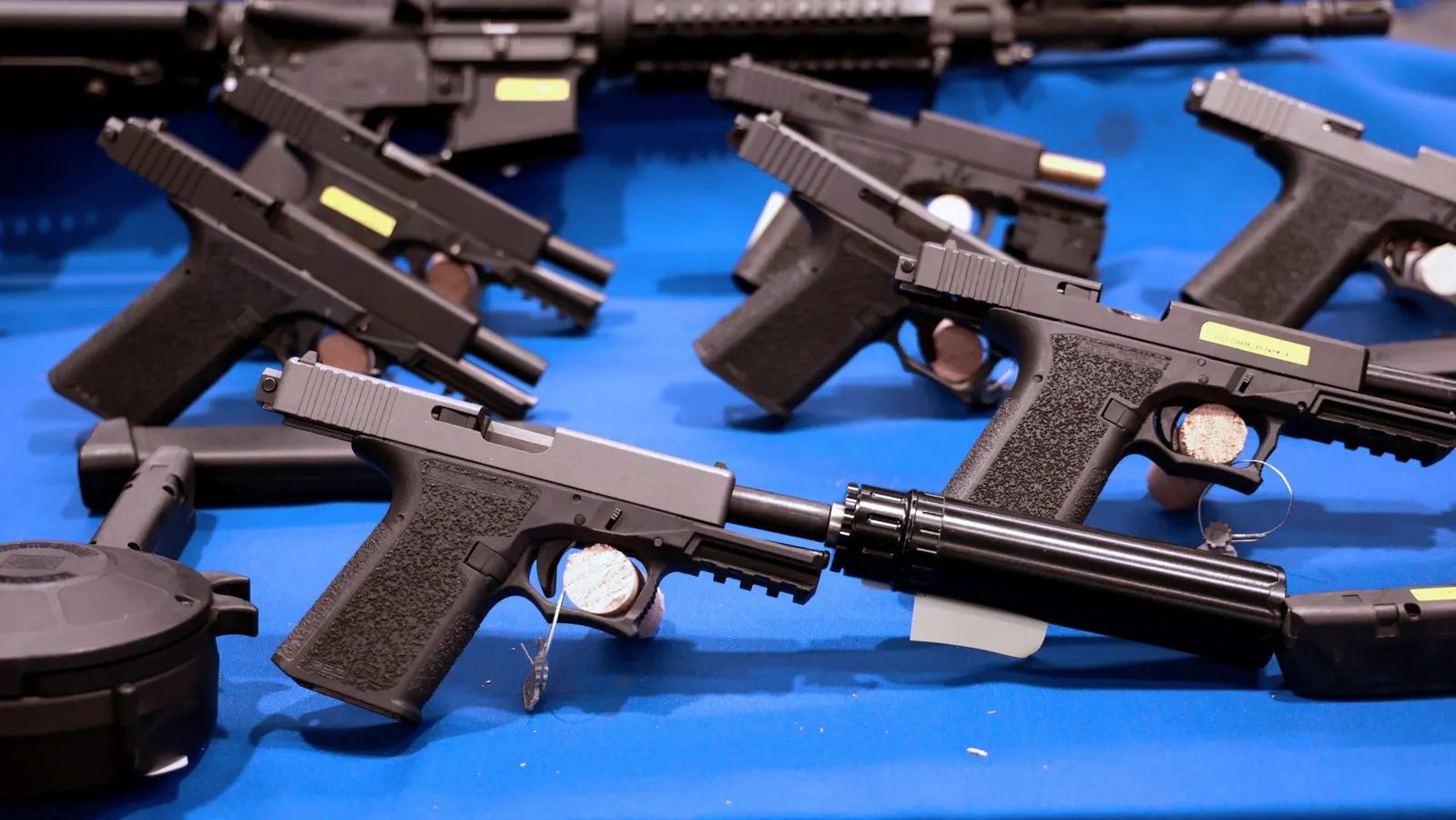
Ghost Guns and the Shocking CEO Shooting: Unraveling Luigi Mangione's Story
Luigi Mangione, accused of killing UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson, allegedly used a "ghost gun," a type of untraceable firearm often assembled at home using 3D-printed parts. These guns, lacking serial numbers, are becoming easier to obtain, raising concerns about their use in crimes. The Biden administration's policy to regulate ghost guns is currently being challenged in the Supreme Court. Between 2016 and 2021, over 45,000 ghost guns were recovered from crime scenes, highlighting the growing issue.