Unraveling the Mystery: Scientists Uncover the Mechanism Behind Aspirin's Efficacy.
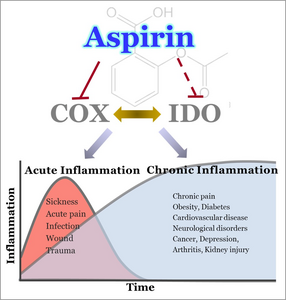
Scientists have discovered more about how aspirin works, including its mechanism of action and cellular targets. Aspirin inhibits the cyclooxygenase enzyme, or COX, which creates messenger molecules crucial in the inflammatory response. The researchers found that aspirin controls transcription factors required for cytokine expression during inflammation while also influencing many other inflammatory proteins and noncoding RNAs that are critically linked to inflammation and immune response. They also showed that aspirin slows the breakdown of the amino acid tryptophan into its metabolite kynurenine by inhibiting associated enzymes called indoleamine dioxygenases, or IDOs. Aspirin's potential interplay between COX and IDO1 during inflammation suggests that COX inhibitors might also be useful as drugs for immunotherapy.
Reading Insights
0
1
3 min
vs 4 min read
82%
633 → 112 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on EurekAlert