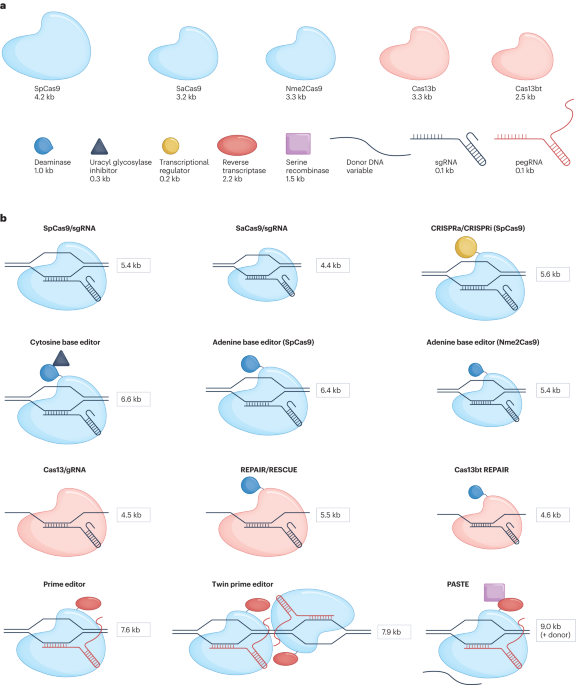
Advancements in CRISPR-based genome editor drug delivery systems
Researchers have explored various drug delivery systems for CRISPR-based genome editing, which holds promise for therapeutic applications. Studies have focused on ex vivo cell-based editing, lentiviral vectors, engineered zinc finger nucleases, TALENs, and the bacterial origins of the CRISPR revolution. The development of CRISPR-Cas systems has revolutionized genome engineering, with applications ranging from gene editing to gene regulation and epigenome editing. Recent advancements include base editors, prime editors, and twin prime editing, enabling precise genomic modifications without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Additionally, researchers have explored mRNA-encoded activators for robust and durable gene activation in vivo. These advancements pave the way for potential breakthroughs in gene therapy and precision medicine.
