"Promising Gene Variant Unveiled: Potential Breakthrough in HIV Treatment for Africans"
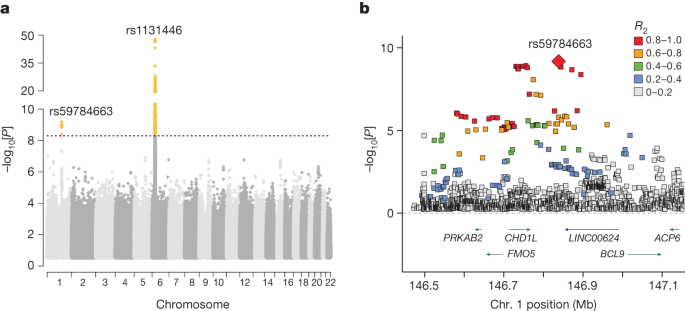
A study has found that Africa-specific human genetic variation near the CHD1L gene is associated with HIV-1 viral load. The research, which analyzed data from over 3,000 individuals, revealed that certain genetic variants near CHD1L were linked to higher viral loads in HIV-positive individuals of African descent. This finding highlights the importance of considering population-specific genetic factors in understanding HIV-1 infection and its progression.
