Emerging Multidrug-Resistant Bacterium in Community Settings: NIH Investigation
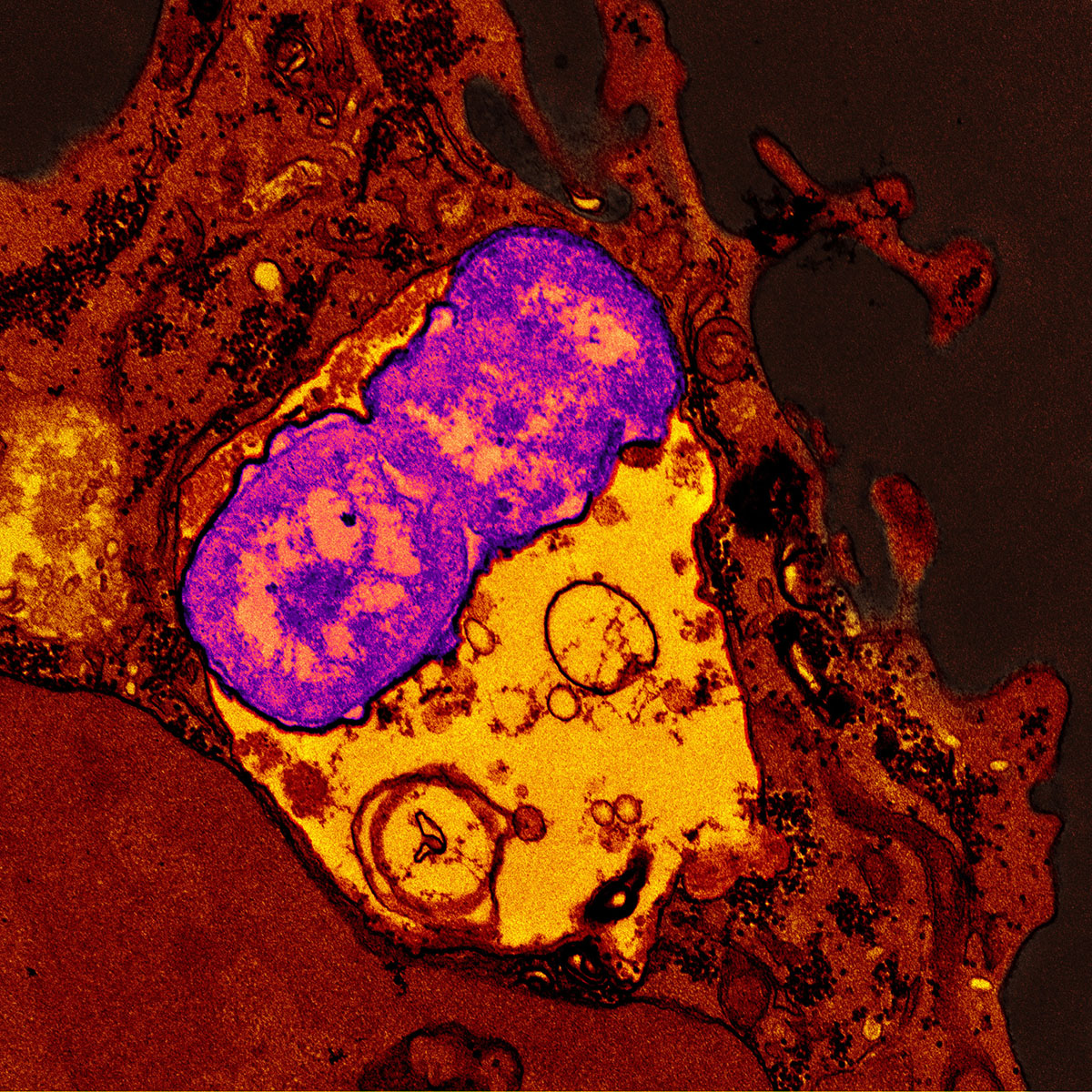
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is investigating the emergence of "hypervirulent" strains of the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae in healthy individuals in community settings. Researchers found that some strains were more likely to survive in blood and serum than others, and that neutrophils (white blood cells) were more likely to ingest and kill certain strains. The study suggests that a vaccine approach for prevention and treatment of infections is feasible. The findings also challenge the classification of K. pneumoniae into classical or hypervirulent forms, and further research will explore the factors involved in the susceptibility of multidrug-resistant hypervirulent strains to the body's immune defenses.
- NIH investigates multidrug-resistant bacterium emerging in community settings National Institutes of Health (.gov)
- Surgical site infection and antimicrobial prophylaxis prescribing profile, and its determinants among hospitalized patients in Northeast Ethiopia: a hospital based cross-sectional study | Scientific Reports Nature.com
- View Full Coverage on Google News
Reading Insights
0
1
3 min
vs 4 min read
86%
750 → 104 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on National Institutes of Health (.gov)