"Enhancing mRNA Vaccine Stability for Efficient Cell Delivery"
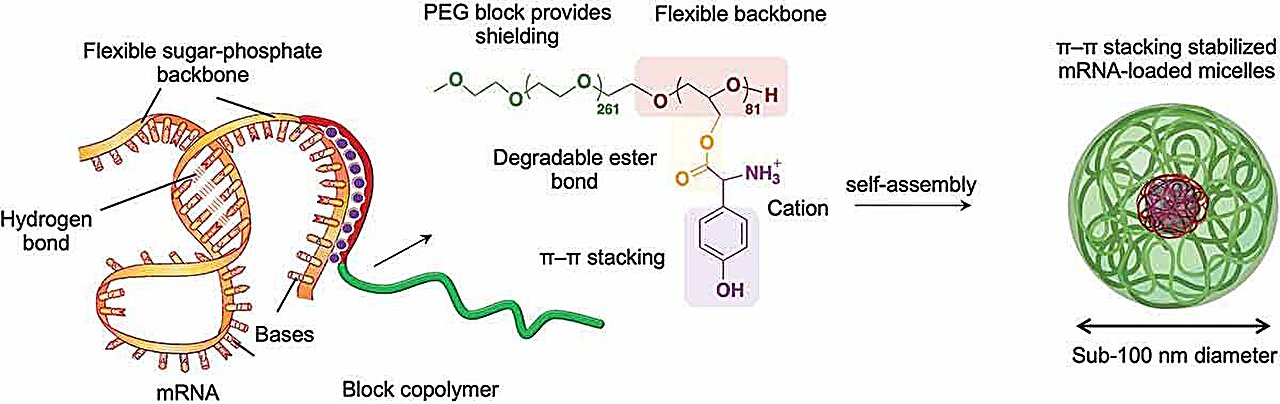
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have developed non-toxic polymers that can stabilize and deliver mRNA into cells more effectively, potentially revolutionizing mRNA-based therapies. By fine-tuning the structure of the polymer molecules and attaching specific positively charged amino acid groups, the mRNA was stabilized and delivered into cultured human cells and live mouse cells with high efficiency. This breakthrough could lead to improved mRNA delivery technologies, innovative release strategies, and enhanced stability and efficacy in mRNA-based therapies for various treatments beyond infectious diseases.
